Bite-Sized Cyber Essentials: Password Practices and Password Managers

This article is part of our Bite-Sized Cyber Essentials Guide, which is designed to help anyone understand the essential information they need to incrementally level up privacy and security - at work and at home.
Password Practices and Password Managers
If we were to think in terms of pure brute force password cracking, a typical password chart looks like the following. The information in each box represents the estimated amount of time it would take to hack each password through a brute force attempt.
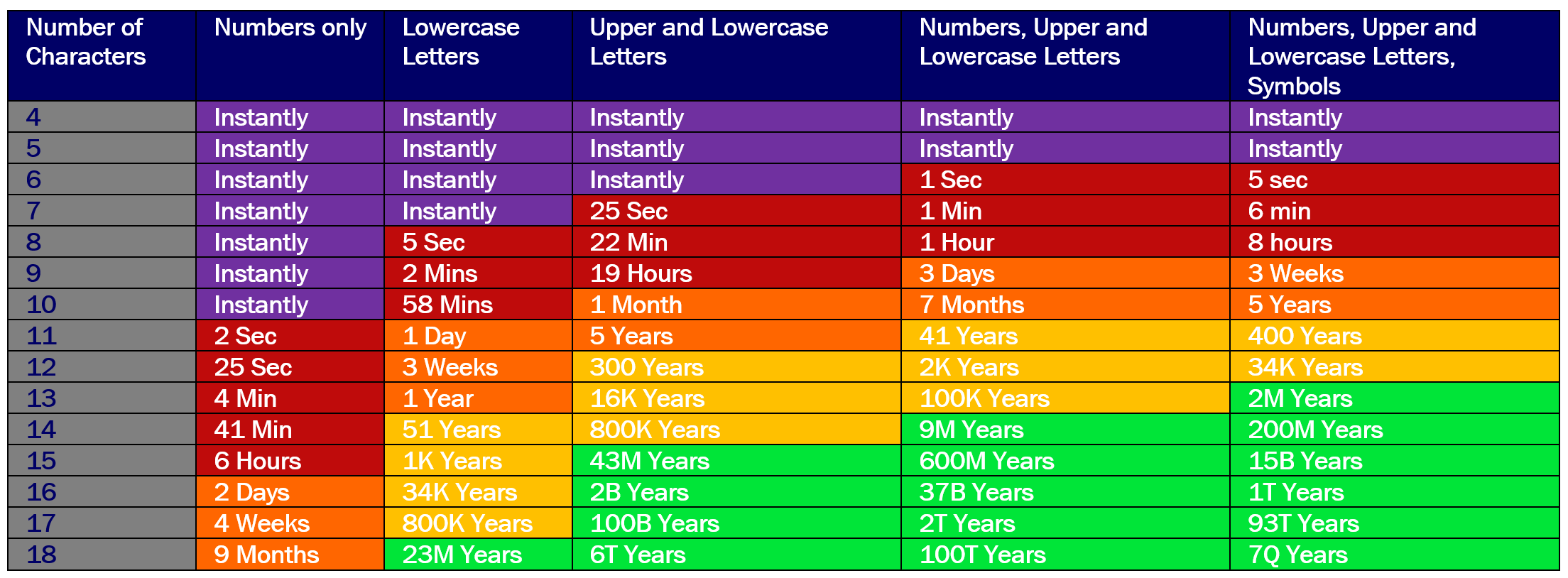
Unfortunately, there are smarter and more efficient ways to crack passwords. In reality, the password chart should probably look like this.
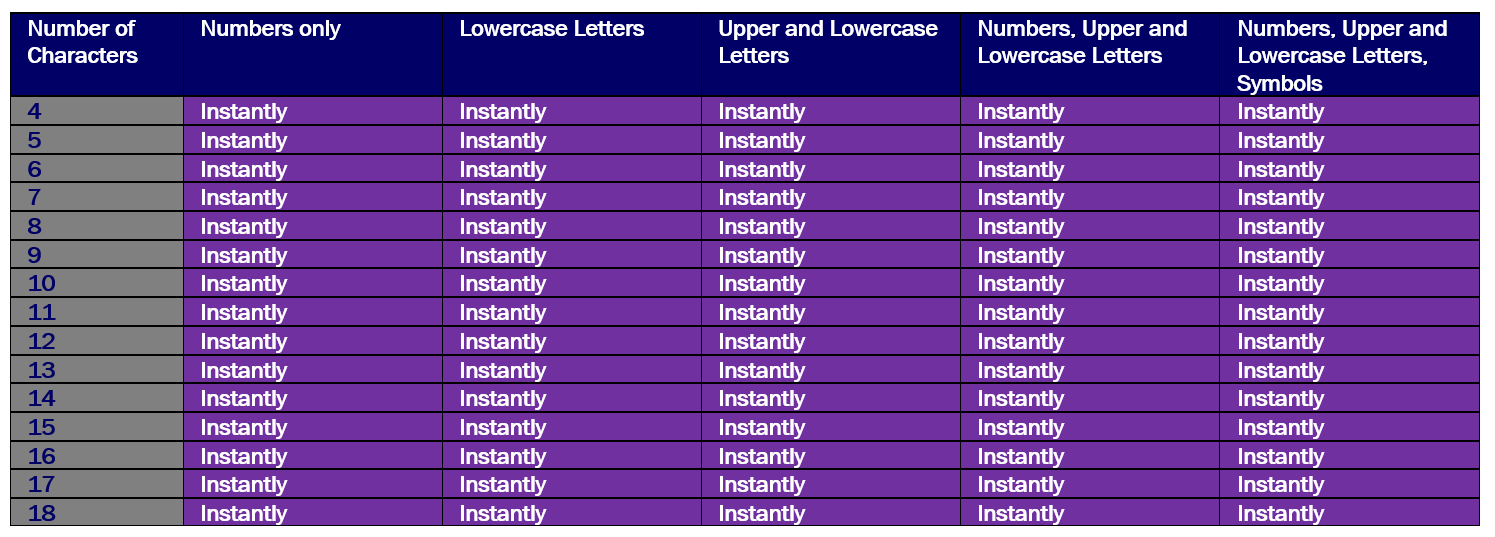
While it may seem like there is nothing that can be done, this is not the case! There are smart and effective ways to create (and manage) passwords that reduce the likelihood of a personal account becoming compromised.

| 
|
Things to Avoid
| Things to Consider
|
Selecting a Password Manager
Having more secure passwords is a great start, but even the best passwords are still at risk if they are all stored in a spreadsheet or notes app.
In addition to having safer and more secure password practices, it is important to understand how password managers work.
Remember: Just because a password manager suffers a security incident [1] does not mean your passwords, and everything stored there, are compromised!!
Using a safe and secure password manager that follows proper and mature security practices is still much safer than storing notes inside a browser directly, in notes, or a spreadsheet.
The following is a representative list of password managers and is not meant as a recommendation or a comprehensive list. We’ve included it here to help our readers understand what types of features we recommend that you look for when evaluating the best password manager for you. Pricing is current as of research date on 12 Oct 2022 - users should check for updated pricing.
| PRICE PLAN | ENCRYPTED VAULT | COMPLIANCE | TRANSPARENCY | ADDITIONAL FEATURES | |
 KEEPASS | Entirely free | AES-256-bit encryption Database files are encrypted | OSI certified | Open source | Supports offline use |
 BITWARDEN | Personal: Free Premium: ~$1/mo Families: ~ $3.33/mo + Business pricing options | AES-256-bit encryption End-to-end encryption | GDPR CCPA HIPPA EU-US Privacy Shield SOC2 & SOC3 | Bug bounty program | Supports offline use Cross platform |
 KEEPER | Personal: $2.92/mo Families: $6.25/mo Students: 50% off Medical & Military: 30% off + Business pricing options | AES-256-bit encryption Local encrypted key | GDPR CCPA HIPPA EU-US Privacy Shield ISO27001 SOC2 Additional certifications & compliance here | Penetration testing Incident response report Bug bounty program | Cross platform Dark web monitoring |
 1PASSWORD | Personal: $2.99/mo Families: $4.99/mo + Business pricing options | AES-256-bit encryption Local encrypted key | SOC2 | Penetration testing Incident response report Bug bounty program | Clipboard management Cross platform Dark web monitoring |
When it comes to password managers, use multifactor authentication (MFA) on the master password as well!
--
[1] Often the term “data breach” is used whenever a there is a security incident. It is important to distinguish that a breach refers to when a certain amount of personally identifiable information is accessed or mishandled whereas a security incident refers to a violation or imminent threat of violation of security policies, acceptable use policies, or standard security practices. https://www.linkedin.com/posts/dan-desko_was-lastpass-actually-breached-or-did-they-activity-6970780468052983808-rpe8
