Cyber Intelligence Weekly (March 24, 2024): Our Take on Three Things You Need to Know
Welcome to our weekly newsletter where we share some of the major developments on the future of cybersecurity that you need to know about. Make sure to follow my LinkedIn page as well as Echelon’s LinkedIn page to receive updates on the future of cybersecurity!
To receive these and other curated updates to your inbox on a regular basis, please sign up for our email list here: https://echeloncyber.com/ciw-subscribe
Before we get started on this week’s CIW, I’d like to highlight the various roles that we have open over here at Echelon! Please check out our LinkedIn page to see all the great roles and apply today!
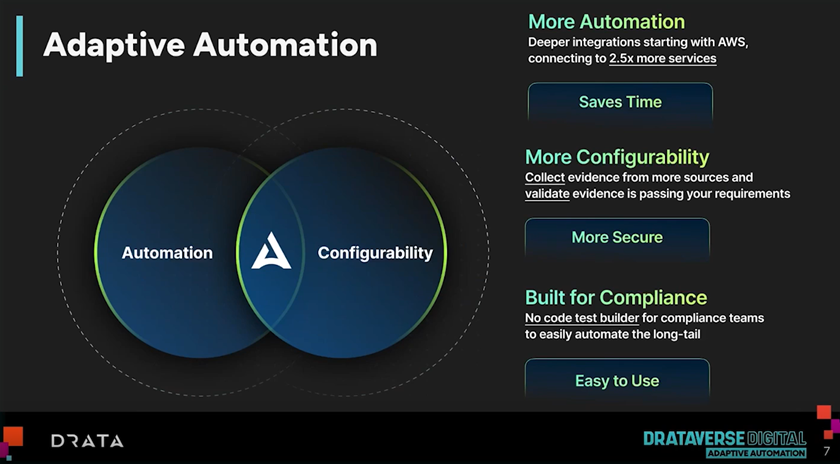
Drataverse Digital Update - Adaptive Automation & More!

Echelon Risk + Cyber proudly cultivates a diverse network of strategic relationships with leading vendors in the Cybersecurity Industry. These collaborations empower Echelon to deliver premium services to our clients through cutting-edge technology and valuable insights. In our ongoing effort to bring top-shelf knowledge, each week, we want to spotlight a distinguished partner solution offered at Echelon. This week’s focus is on Drata’s recent release of Adaptive Automation.
The unveiling of Adaptive Automation by Drata heralds the introduction of five pivotal features within their Compliance Platform: Adaptive Automation, AI-generated third-party risk report cards, Central Risk Assessment 2.0, New FedRAMP Framework, and User Access Reviews Expansion.
Beginning with Adaptive Automation, this innovative feature empowers users to harness new test sources and custom logic to construct automated, no-code AWS tests within Drata. This capability facilitates the creation of custom condition groups and filtering criteria to scrutinize AWS controls and ensure comprehensive compliance.
The introduction of AI-generated third-party risk report cards streamlines the process of summarizing and identifying vendor risks using advanced AI technology. Driven by Drata's cutting-edge AI engine, this feature automates the evaluation of vendor security questionnaires, distilling crucial insights and highlighting pertinent information effortlessly.
Central Risk Assessment 2.0 represents a significant enhancement, enabling the creation of a central risk register comprising over 150 pre-mapped risks aligned with compliance controls, facilitating seamless integration and sharing of risk statuses. This update introduces four key upgrades:
- Risk Library: Offering a comprehensive selection of over 200 risks for consideration, users can seamlessly incorporate chosen risks into the risk register.
- Custom Risks: Within the Risk Library, users have the flexibility to define custom risks, including titles, descriptions, assessments, and treatments tailored to specific risk scenarios.
- Assign Owners: Assigning owners to specific risks ensures accountability, encompassing risk scoring and management throughout the lifecycle, including treatment planning.
- Risk Register: By providing a consolidated view of selected risks from the Risk Library, users can define impact and likelihood parameters, allowing Drata to calculate inherent risk scores. Additionally, the Risk Register facilitates the mapping of risks to a visual Risk Posture, enabling organizations to gauge the potential impact of low, medium, high, and critical risks.
Furthermore, Drata now incorporates the FedRAMP Framework, facilitating organizations in streamlining the journey toward FedRAMP readiness and compliance. Customizable baselines tailored to organizational needs and pre-packaged controls aid in meeting FedRAMP compliance requirements efficiently.
Lastly, the User Access Reviews Expansion bolsters support for M365 and Google Direct, streamlining the access review process for enhanced efficiency and security. With the conclusion of the insight into Drata’s recent release of Adaptive Automation, we look ahead with anticipation. Echelon Risk + Cyber remains dedicated to pushing the boundaries of cybersecurity innovation, forging partnerships that empower us to stay at the forefront of industry trends. If your organization is grappling with specific security challenges, allow Echelon to help alleviate the burden. Reach out to discuss how we might help your organization, and stay tuned for more solution highlights in the weeks to come!
Away we go!
1. Apple's M-Series Chips Exposed: The Unpatchable GoFetch Vulnerability
A groundbreaking vulnerability discovered in Apple's M-series chips has raised alarms across the cybersecurity community. Researchers have identified an un-patchable side-channel vulnerability that allows attackers to extract secret encryption keys by exploiting the chips' microarchitectural design. This flaw is inherent to the design of the silicon itself, meaning it cannot be fixed with a simple software update. Instead, mitigation efforts would require significant modifications to third-party cryptographic software, potentially leading to considerable performance degradation, especially on the M1 and M2 chip generations. This vulnerability is particularly concerning due to its exploitation of the chips' data memory-dependent prefetcher (DMP), a feature designed to improve performance by predicting and loading likely-needed data into the CPU cache ahead of time.
The exploitation technique, dubbed GoFetch by the researchers, leverages the DMP's behavior of confusing memory content with pointer values, causing unauthorized data leakage. This method represents a serious breach of the constant-time programming paradigm, a defense against side-channel attacks that ensures cryptographic operations take the same amount of time regardless of the data involved. GoFetch can be executed without needing root access, using applications with normal user privileges, and is capable of extracting keys from classical encryption algorithms as well as those designed to be resistant to quantum computing attacks. The researchers demonstrated that GoFetch could extract keys within hours, underscoring the practical threat posed by this vulnerability.
Mitigating this vulnerability presents a complex challenge, with most solutions imposing a heavy toll on performance. Options like ciphertext blinding, while effective, can significantly increase the resources needed for cryptographic operations. An alternative might be running cryptographic processes on the chip's efficiency cores, which lack DMP but would also likely slow down operations. Apple's latest M3 chip introduces a potential mitigation by allowing developers to disable the DMP, but the performance implications of this are still unclear. This vulnerability highlights the ongoing tension between advancing hardware performance and ensuring cybersecurity, prompting a reevaluation of how sensitive cryptographic operations are handled on modern processors.
2. Securing the Flow: The U.S. Urges Ramp Up of Cyber Defenses for Water Systems
The White House and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), has issued a stark warning to all states about the growing threat of cyberattacks targeting the nation's water systems. In a proactive move to enhance the cybersecurity posture of water and wastewater utilities, the Biden administration has highlighted concerns over attacks, particularly those linked to Iranian and Chinese government hackers. These cyber intrusions not only threaten the availability of clean drinking water but also bear the potential to incur significant financial burdens on the communities affected. To address these vulnerabilities, a collaborative meeting involving key department secretaries is scheduled for March 21st, aiming to fortify the defenses of critical water infrastructure against such cyber threats.
In addition to raising awareness about the risks, the EPA is spearheading the formation of a Water Sector Cybersecurity Task Force. This initiative seeks to pinpoint security gaps and apply insights from the upcoming discussion to shield the water sector from digital adversaries. The letter sent to U.S. governors underscores the importance of implementing basic cybersecurity measures, such as changing default passwords and updating software to rectify known weaknesses, which could dramatically reduce the risk of a successful cyberattack. The urgency of these measures was compounded by recent incidents, including attacks by Iranian hackers on water facilities using unchanged default passwords and the exposure of U.S. drinking water system information by the Chinese state-sponsored group, Volt Typhoon.
This collective effort by the U.S. government to ramp up cybersecurity in the water sector underscores the critical nature of protecting such essential infrastructure. By fostering a coordinated response among federal, state, and local entities, and promoting the adoption of fundamental cyber hygiene practices, the initiative aims to safeguard public health and safety against the backdrop of an increasingly hostile cyber landscape.
3. Hotel Havoc, Hackers Can Open Millions of Rooms in Seconds
A team of researchers has uncovered a significant vulnerability in the Saflok-brand RFID keycard locks, which are used in millions of hotel rooms worldwide. This discovery, made by Ian Carroll, Lennert Wouters, and their colleagues, highlights a technique known as Unsaflok that exploits weaknesses in both the encryption used by Dormakaba, the Swiss manufacturer of these locks, and the underlying RFID system, MIFARE Classic. The vulnerability allows attackers to gain access to any room secured by these locks within seconds by creating two specially crafted keycards or signals, following a relatively simple process that does not require specialized access privileges.
Dormakaba has been notified of the vulnerabilities and has been working with hotels to address the security flaws without the need for a hardware replacement in most cases, focusing instead on updating the management systems and reprogramming each lock. Despite these efforts, the researchers have been informed that only a fraction of the affected locks have been updated, pointing to a potentially lengthy process for fully securing the locks against this exploit. This situation underscores the challenges of securing widely used physical security systems and the importance of continuous vigilance in the face of evolving cyber threats.
The discovery of the Unsaflok vulnerability serves as a stark reminder of the persistent risk posed by even the most seemingly secure technologies. As the researchers and Dormakaba work towards a resolution, hotel guests are advised to remain cautious and take additional precautions to safeguard their belongings and privacy. The case also emphasizes the broader implications of cybersecurity research and the delicate balance between exposing vulnerabilities to prompt action and the risk of providing a roadmap for malicious actors.
Thanks for reading!
About us: Echelon is a full-service cybersecurity consultancy that offers wholistic cybersecurity program building through vCISO or more specific solutions like penetration testing, red teaming, security engineering, cybersecurity compliance, and much more! Learn more about Echelon here: https://echeloncyber.com/about

